
Resting Echocardiogram
What is a resting echo?
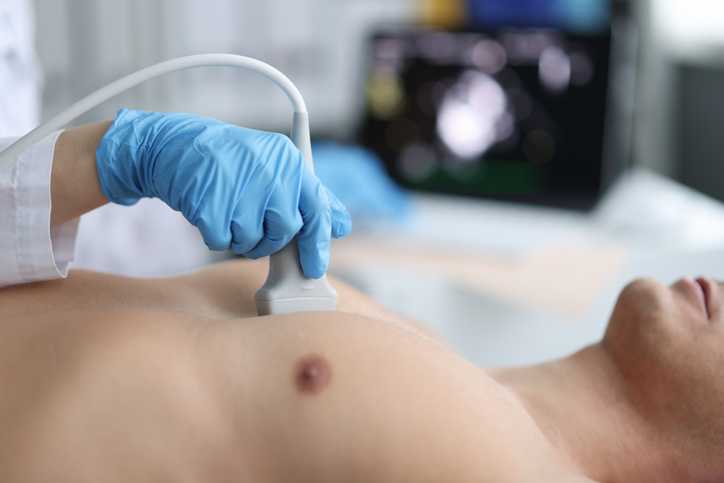
An echocardiogram, also known as an echo, is the most common type of heart ultrasound. Your doctor uses it to assess the health of your heart. The ultrasound shows images of your heart beating, the structure of your heart and how well blood is pumped through your heart chambers, and valves. These images can reveal heart defects or irregularities.
Other types of echocardiogram are a stress echo, which compares your heart before and after exercise; a dobutamine stress echo, which uses medication to simulate the effects of exercise; and a transoesophageal echo, which uses a tube inserted down your oesophagus to record images of your heart.
Why do I need a resting echo?
There are a number of reasons why your doctor may refer you for an echo. Four common reasons include:
- You have been experiencing signs or symptoms of heart disease, such as shortness of breath or chest pain.
- Your doctor may have detected an abnormal heart murmur or irregular heartbeat in your examination or other tests.
- Your doctor may want information about your heart’s ability to pump.
- You are already undergoing treatment for a specific condition, and your doctor wants to monitor your heart.
What happens during a resting echo?
What happens during a resting echo?
Echocardiogram
What to expect

An echo is a painless, non-invasive test. If your lungs or ribs block the view of your heart, you may need a small amount of a saline solution injected through an intravenous (IV) line. This will mean your heart’s structure will show up more clearly on the screen.
The test should take around 45 minutes in total and no recovery time is needed.
- You’ll need to remove your clothes from the waist up and wear a provided gown.
- You’ll be asked to lie on your left side on an examination bed.
- If your doctor is using a saline solution, they will inject the solution.
- A cardiac sonographer will attach small metal disks, called ECG electrodes, to your chest. These electrodes attach to a machine that monitors your heart rhythm during this test.
- A cool gel will be placed on your skin and the sonographer will move a handheld wand across your chest to take the ultrasound images of your heart.
- You may be asked to hold your breath briefly or change position.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I prepare for my test? What's involved?
You don’t need any special preparation before a resting echo, and you can eat and drink as you usually would.
What should I do on the day of the test?
- Bring a list of your current medications.
- Wear a shirt or blouse, as you will need to undress to the waist. You will be provided with a gown for privacy.
- Do not apply any lotions or powders to your chest area and don’t wear neck jewellery.
What happens after a resting echo?
- You can resume your normal activities straight after the echo.
- One of our cardiologists will review your results and provide a full report to your referring doctor, who will contact you for the next steps.
Is a resting echo safe?
This test is non-invasive. They don’t use radiation, unlike X-rays.
What do the results of a resting echo mean?
The results can reveal many different things about your heart health. These may include:
- If there’s a change in the size or thickness of the heart’s chambers.
- Heart defects.
- Damage to the heart muscle.
- Stiffness of the heart.
- Any blood clots in the heart’s chambers.
- Pressure in the heart.
- Any fluid in the sac around the heart.
- Issues with the pumping or relaxing function of the heart.
- Any problems with the function of the heart valves.

How Do I Make An Appointment?
If you have a referral from your GP, click here to make an appointment at your nearest centre.
This information is of a general nature. If you are concerned about your heart health, discuss this with your local doctor.

